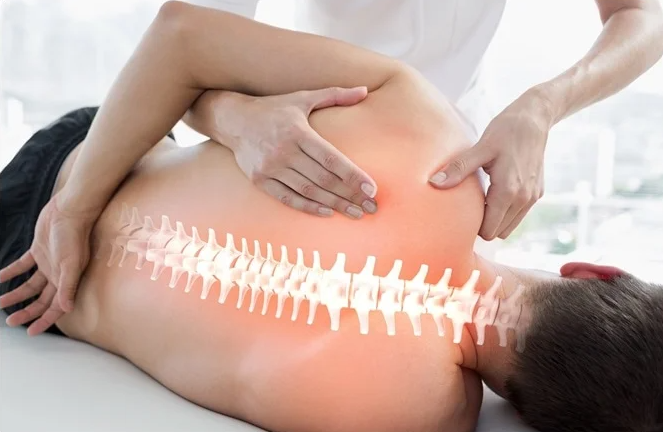
In physiotherapy, trained professionals evaluate and treat abnormal physical functions in the body. They can be associated with, for example, injury, disability, or disease.
- Physiotherapy – what is it?
- Physiotherapy – what does it help?
- Physiotherapy – benefits
- Physiotherapy – types
Physiotherapy – what is it?
A physical therapist helps care for patients at all stages of treatment, from the initial diagnosis to regenerative and preventive stages of recovery. Physiotherapy can be a standalone option or support other treatments. Some patients are referred by their doctor to a physiotherapist, but others undergo this therapy themselves.
Regardless of how the patient goes to the physiotherapist, he or she can:
- Receive a physical examination and evaluation, including your health history and certain testing procedures, including evaluation of posture, movement and flexibility, and muscle and joint movement and performance
- Obtain a clinical diagnosis, prognosis, care plan, and short- and long-term goals
- Receive treatment and physiotherapeutic intervention based on therapist assessment and diagnosis
- Receive recommendations for self-care.
Patients often train with a physical therapist about exercises they can do at home to improve musculoskeletal function.
Physiotherapy – what does it help?
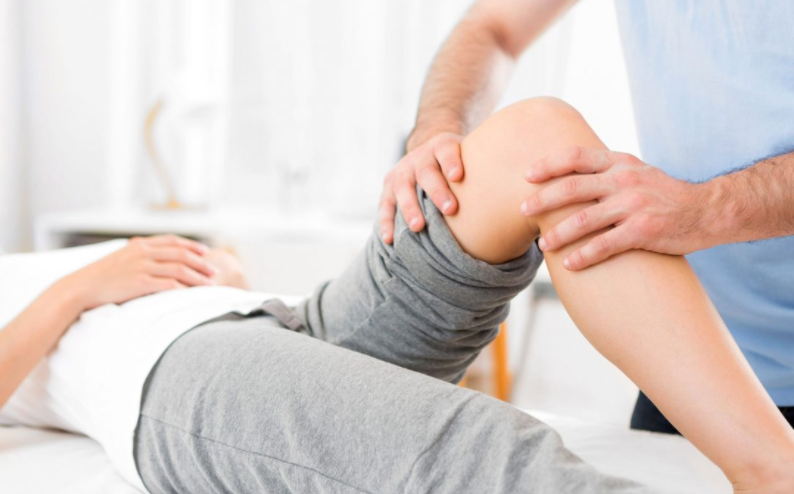

Physiotherapists can help in the treatment of a variety of diseases, depending on their specialization. Patients who may benefit from this type of treatment usually develop:
- Cardiopulmonary diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis), and post-myocardial infarction (MI)
- Diseases such as carpal tunnel syndrome and trigger finger (hand therapy)
- Musculoskeletal dysfunctions such as back pain, temporomandibular joint disorders
- Neurological conditions such as stroke, spinal cord injuries, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, vestibular dysfunction, and brain injuries
- Pediatric diseases such as developmental delay, cerebral palsy, and muscular dystrophy
- Sports-related injuries such as concussion and tennis elbow
- Reproductive diseases and pelvic floor disorders such as urinary incontinence and lymphedema.
Other cases where physical therapy may benefit include burns, wound healing, and diabetic ulcers.
Physiotherapy – benefits
Depending on the reason for treatment, the benefits of physical therapy include:
- Pain management with reduced opioid requirements
- Avoiding surgery
- Improved mobility and movement
- Recovery after an injury or trauma
- Recovery from stroke or paralysis
- Fall prevention
- Better balance
- Age-related health problems management.
A sports therapist can help an athlete maximize athletic performance by strengthening specific parts of the body and using muscles in new ways.
Physiotherapy – types

Physiotherapy can help a patient regain movement or strength after an injury or illness. As with any field of medicine, a variety of treatments can be used to treat a wide variety of conditions.
Orthopedic physical therapy treats musculoskeletal injuries that involve muscles, bones, ligaments, fascia, and tendons. It is used to treat conditions such as fractures, sprains, tendinitis, bursitis, and chronic health problems. Rehabilitation after orthopedic surgery is also possible. Patients can be treated with joint mobilization, manual therapy, strength training, mobility training, and other methods.
Geriatric physiotherapy can help elderly patients with conditions that affect their mobility and physical function, including arthritis, osteoporosis, Alzheimer’s disease, hip and arthroplasty, balance disorders, and urinary incontinence. This type of intervention is designed to restore mobility, reduce pain and increase levels of fitness.
Neurological physiotherapy can help people with disorders and neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, brain injury, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injury, and stroke. Treatment may be aimed at increasing the responsiveness of the limbs, treating paralysis, and reversing the increase in muscle strength by reducing muscle atrophy.
Cardiovascular and pulmonary rehabilitation can benefit those affected by certain cardiopulmonary diseases and surgery. Treatment can increase your physical endurance and endurance.
Pediatric physical therapy aims to diagnose, treat, and treat diseases that affect infants, children, and adolescents, such as developmental delays, cerebral palsy, spina bifida, torticollis, and other conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system.
Wound therapy (care) can help ensure that the wound heals receives adequate oxygen and blood by improving circulation. Physiotherapy can include manual therapies, electrical stimulation, compression therapy, and wound healing.
Vestibular stimulation aims to treat balance problems that can result from diseases of the inner ear. Vestibular physical therapy includes a range of exercises and manual techniques that can help patients regain balance and coordination.
Lymphatic drainage can help drain accumulated fluid in patients with lymphedema and other conditions where fluid accumulates.
Pelvic floor rehabilitation can help treat urinary or fecal incontinence, urge to urinate, and pelvic pain in men and women as a result of an injury or surgery, or due to certain medical conditions.
In addition to exercise, physical therapy may include:

Ultrasound , which improves blood flow and healing by heating tendons, muscles and tissues
Phonophoresis , which uses ultrasound to deliver certain medications, such as topical steroids. This can reduce the presence of inflammation
Electric stimulation or E-stimulation, which uses local electrodes on the skin to reduce pain and increase functional capabilities. One type of E-stimulation is Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS). Sometimes, anti-inflammatory drugs are used with specific electrical stimulation methods and this is referred to as iontophoresis.
Heat and cold therapy
Light therapy in which special lights and lasers are used to treat specific medical conditions
The physiotherapist will recommend the most appropriate treatment.